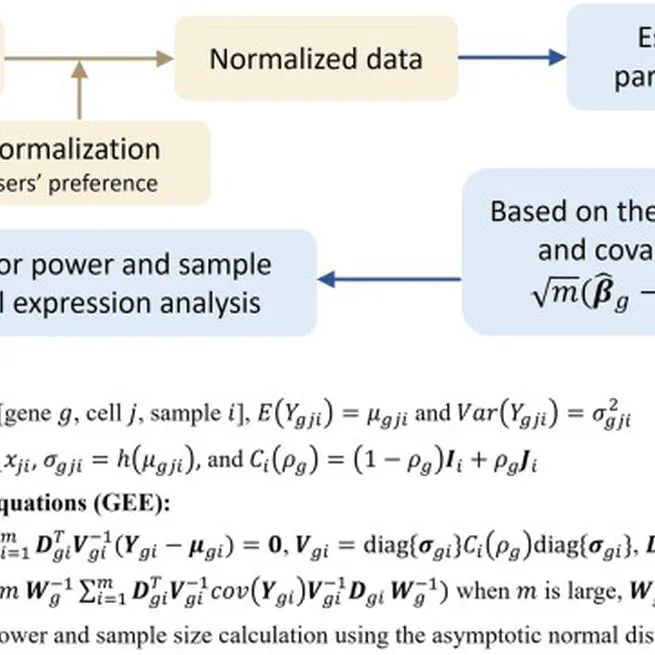
power and sample size estimation for single-cell transcriptome
Sep 4, 2024
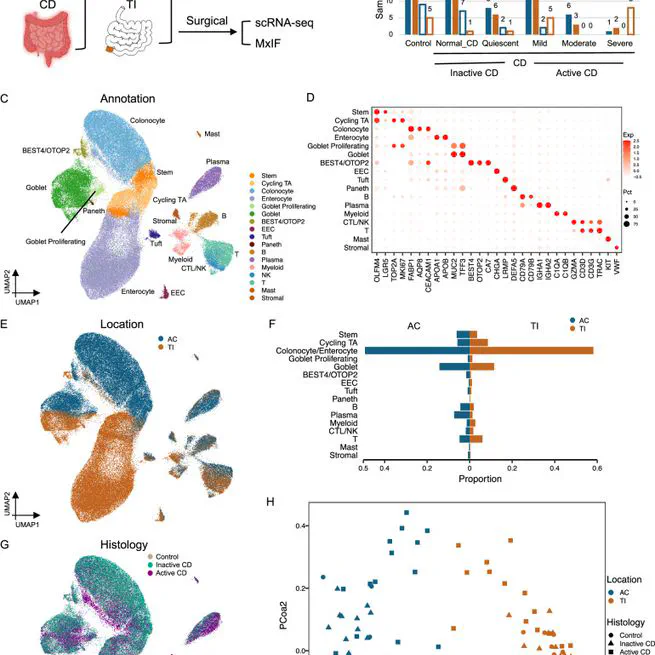
Abstract Crohn’s disease (CD) is a complex chronic inflammatory disorder with both gastrointestinal and extra-intestinal manifestations associated immune dysregulation. Analyzing 202,359 cells from 170 specimens across 83 patients, we identify a distinct epithelial cell type in both terminal ileum and ascending colon (hereon as ‘LND’) with high expression of LCN2, NOS2, and DUOX2 and genes related to antimicrobial response and immunoregulation. LND cells, confirmed by in-situ RNA and protein imaging, are rare in non-IBD controls but expand in active CD, and actively interact with immune cells and specifically express IBD/CD susceptibility genes, suggesting a possible function in CD immunopathogenesis. Furthermore, we discover early and late LND subpopulations with different origins and developmental potential. A higher ratio of late-to-early LND cells correlates with better response to anti-TNF treatment. Our findings thus suggest a potential pathogenic role for LND cells in both Crohn’s ileitis and colitis.
Aug 22, 2024
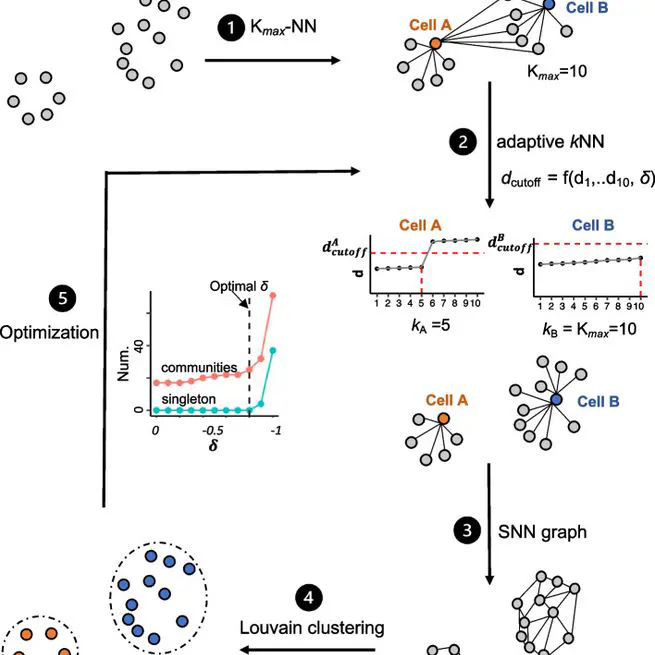
adaptive k nearest neighbor graph for single-cell and spatial clustering
Aug 2, 2024
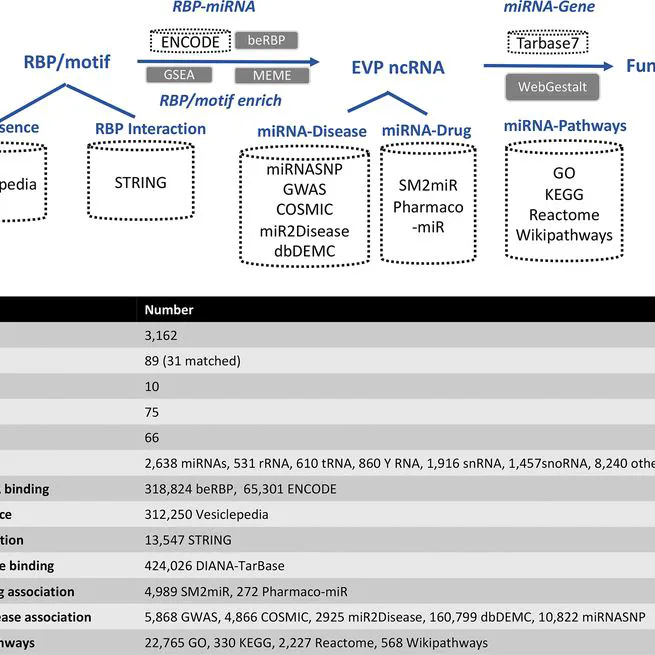
an atlas of non-coding small RNA abundance profiling and sorting in human Extracellular Vesicles and Particles
Apr 12, 2024
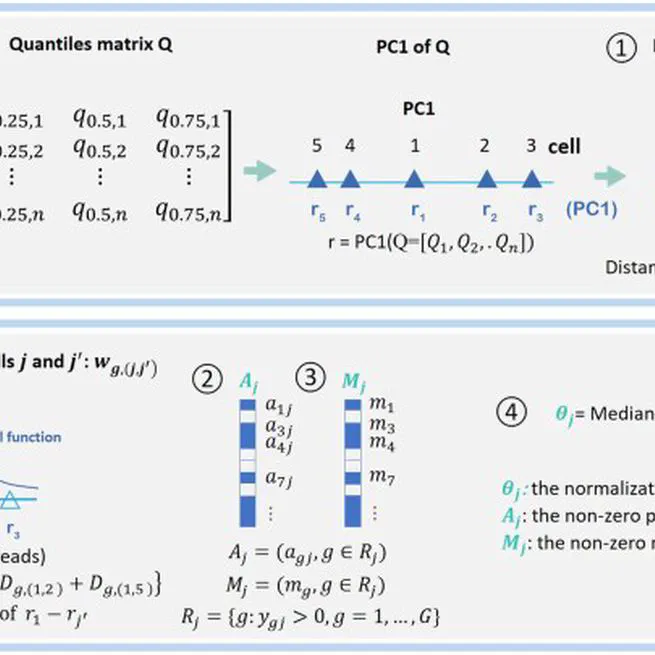
normalization for single-cell transcriptome
Jan 19, 2024
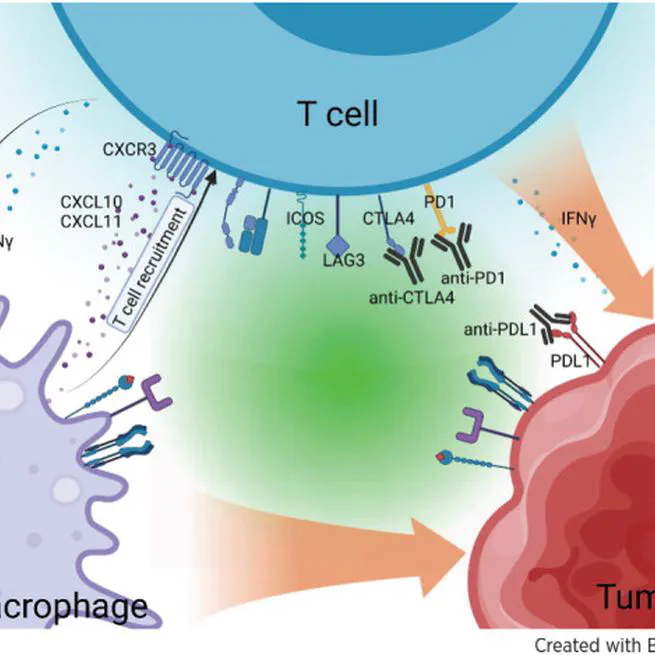
Abstract Although considerable efforts have been dedicated to identifying predictive signatures for immune checkpoint inhibitor (ICI) treatment response, current biomarkers suffer from poor generalizability and reproducibility across different studies and cancer types. The integration of large-scale multiomics studies holds great promise for discovering robust biomarkers and shedding light on the mechanisms of immune resistance. In this study, we conducted the most extensive meta-analysis involving 3,037 ICI-treated patients with genetic and/or transcriptomics profiles across 14 types of solid tumor. The comprehensive analysis uncovered both known and novel reliable signatures associated with ICI treatment outcomes. The signatures included tumor mutational burden (TMB), IFNG and PDCD1 expression, and notably, interactions between macrophages and T cells driving their activation and recruitment. Independent data from single-cell RNA sequencing and dynamic transcriptomic profiles during the ICI treatment provided further evidence that enhanced cross-talk between macrophages and T cells contributes to ICI response. A multivariable model based on eight nonredundant signatures significantly outperformed existing models in five independent validation datasets representing various cancer types. Collectively, this study discovered biomarkers predicting ICI response that highlight the contribution of immune cell networks to immunotherapy efficacy and could help guide patient treatment. SIGNIFICANCE: Identification of robust immunogenomic connections, particularly macrophage T-cell interactions, in a large-scale pan-cancer meta-analysis and development of a predictive model for immunotherapy response that outperformed existing models could facilitate clinical decision-making.
Dec 20, 2023
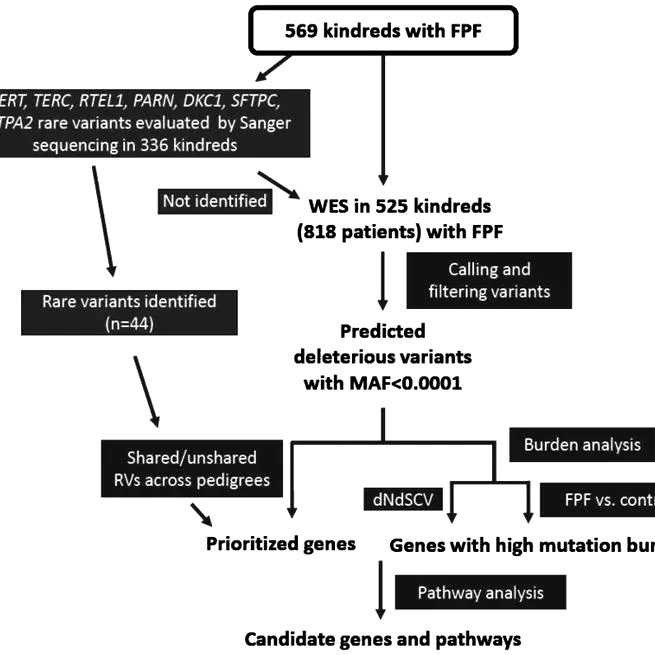
Abstract Rationale and Objectives: Up to 20% of idiopathic interstitial lung disease is familial, referred to as familial pulmonary fibrosis (FPF). An integrated analysis of FPF genetic risk was performed by comprehensively evaluating for genetic rare variants (RVs) in a large cohort of FPF kindreds. Methods: Whole-exome sequencing and/or candidate gene sequencing from affected individuals in 569 FPF kindreds was performed, followed by cosegregation analysis in large kindreds, gene burden analysis, gene-based risk scoring, cell-type enrichment analysis, and coexpression network construction. Measurements and Main Results: It was found that 14.9-23.4% of genetic risk in kindreds could be explained by RVs in genes previously linked to FPF, predominantly telomere-related genes. New candidate genes were identified in a small number of families-including SYDE1, SERPINB8, GPR87, and NETO1-and tools were developed for evaluation and prioritization of RV-containing genes across kindreds. Several pathways were enriched for RV-containing genes in FPF, including focal adhesion and mitochondrial complex I assembly. By combining single-cell transcriptomics with prioritized candidate genes, expression of RV-containing genes was discovered to be enriched in smooth muscle cells, type II alveolar epithelial cells, and endothelial cells. Conclusions: In the most comprehensive FPF genetic study to date, the prevalence of RVs in known FPF-related genes was defined, and new candidate genes and pathways relevant to FPF were identified. However, new RV-containing genes shared across multiple kindreds were not identified, thereby suggesting that heterogeneous genetic variants involving a variety of genes and pathways mediate genetic risk in most FPF kindreds.
Jan 10, 2023
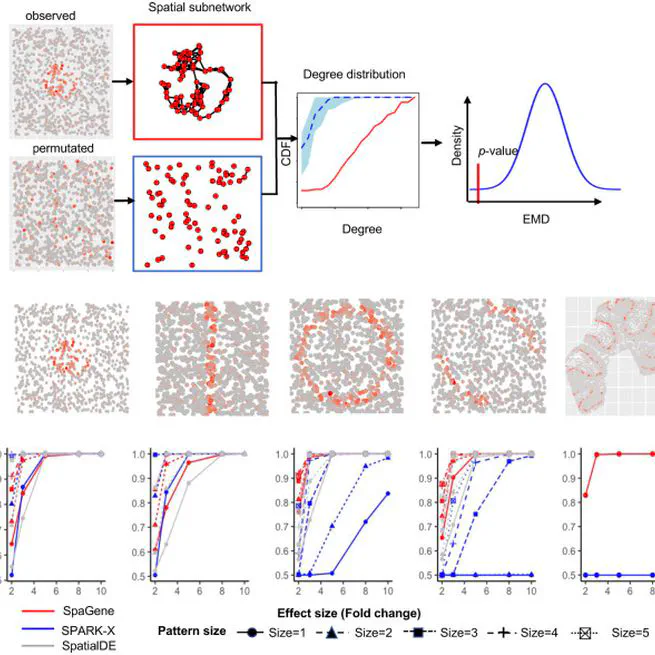
spatial pattern and co-localization
Oct 13, 2022
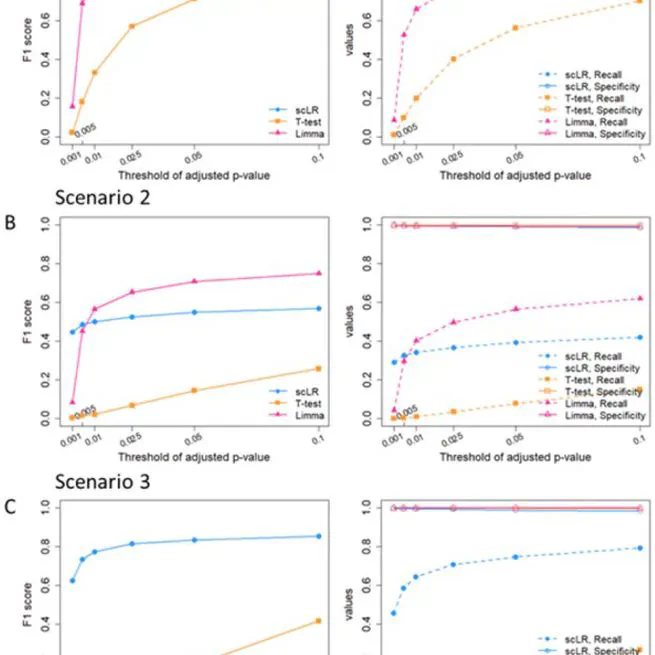
dysregulated ligand-receptor interaction for single-cell data
Apr 29, 2022
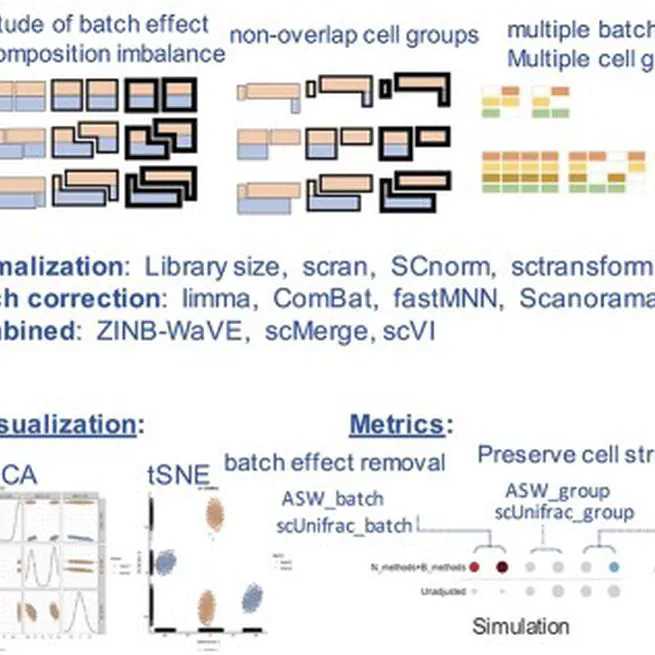
Abstract Normalization and batch correction are critical steps in processing single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq) data, which remove technical effects and systematic biases to unmask biological signals of interest. Although a number of computational methods have been developed, there is no guidance for choosing appropriate procedures in different scenarios. In this study, we assessed the performance of 28 scRNA-seq noise reduction procedures in 55 scenarios using simulated and real datasets. The scenarios accounted for multiple biological and technical factors that greatly affect the denoising performance, including relative magnitude of batch effects, the extent of cell population imbalance, the complexity of cell group structures, the proportion and the similarity of nonoverlapping cell populations, dropout rates and variable library sizes. We used multiple quantitative metrics and visualization of low-dimensional cell embeddings to evaluate the performance on batch mixing while preserving the original cell group and gene structures. Based on our results, we specified technical or biological factors affecting the performance of each method and recommended proper methods in different scenarios. In addition, we highlighted one challenging scenario where most methods failed and resulted in overcorrection. Our studies not only provided a comprehensive guideline for selecting suitable noise reduction procedures but also pointed out unsolved issues in the field, especially the urgent need of developing metrics for assessing batch correction on imperceptible cell-type mixing.
Jan 21, 2022